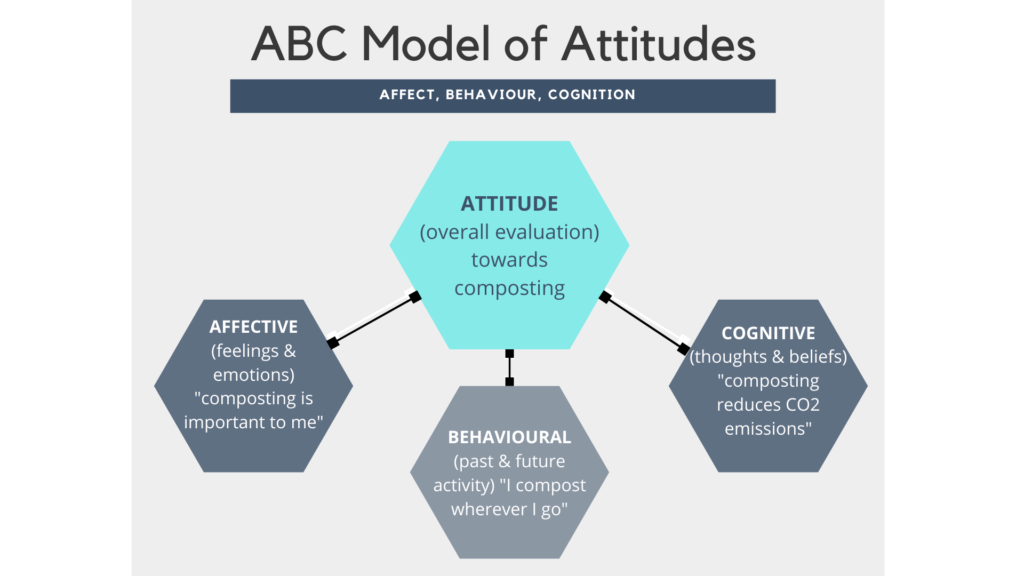
An attitude has 3 different components. Attitude formation has three components.
4 Distinguish between organizational citizenship and workplace deviance behaviours.

. Its goal is to challenge negative beliefs and develop more practical rational ways. As you can see the easy way to recall these components is to use the letters ABC. Utilitarian functionrelates to the basic principles of reward and punishment.
This means that we often or usually expect the behavior of a person to be consistent with the attitudes that they hold. ABC model of attitudes is affect behavior and cognition. Affect refers to the way a consumer feels about an attitude object.
Describe the ABC model of attitudes. We develop attitudes toward products simply because they provide pleasure or pain. Describe the ABC model of attitudes.
List the three hierarchies of attitudes and describe the major differences among them. Regardless attitudes are an important topic of study for social psychologists because they help determine what we do what we eat how we vote what we do with our free time and so on. Whereas A stand for Affect it describe about consumer feels towards attitude object B stand for Behavior it refers to action taken by consumers towards the object and C stand for Cognition it describe what consumers believes.
The basic model of attitude components is the ABC model. Every attitude has three components that are represented in what is called the ABC model of attitudes. Those 3 attitudes is called ABC model of attitudes.
Cognitive refers to the beliefs a consumer has about an attitude object. In CBT the ABC model is a framework for changing irrational thoughts. This study adopts Ostroms ABC model 1969 of attitudes from the domain of so-cial psychology which defines the three components of attitudes as.
A affect B behavior and C cognition. This model is known as the ABC model of attitudes. - Affect feelings - Behaviour actions - Cognitionbeliefs Depending on the nature of the product one of these three components will be the dominant influence in creating an attitude towards a product.
It is often referred to as the ABCs of attitudes and consists of three bases or components affect behavior and cognition. One of the underlying assumptions about the link between attitudes and behavior is that of consistency. Smith in the year 1947 discerned the difference between affective cognitive and policy orientation characteristics of attitude.
Behavior involves the person intention to do something regard to an attitude object an intention does not always result in an actual behavior. Chapter 7 Problem Review_Questions 29. We can remember these three components of an attitude as the ABC model of attitudes.
Affect behavior and cognition. There are three main elements of an attitude. This model of attitudes is known as the ABC-model was first stated by Hovland and Rosenberg 1960 and is today widely accepted by researchers in the field of attitudes and behaviors Solomon et al 2010.
Behavioral intentions with respect to specific attributes or overall object. The ABC Model of Attitudes. 5 Identify the characteristics of the source target and message that affect persuasion.
2 Describe how attitudes are formed. Most researchers agree that an attitude has three components. Originally researchers believed that everyones attitudes contained all three bases but we now know that some attitudes do not contain all.
Affect refers to the way a consumer feels about an attitude object. 3 Identify the sources and consequences of job satisfaction. According to ABC model of attitudes the individuals attitude has three component.
Cognitive component involves the belief or knowledge of the person. Attitudes Emotions and Ethics 1 Explain the ABC model of an attitude. Every attitude has three components that are represented in what is called the ABC model of attitudes.
Behavior involves the persons intentions to do something with regard to an attitude object but as we will discuss at a later point an intention does not always result in an actual behavior. This is called the principle of consistency. ABC refers to affective cognitive and behavioral.
The three hierarchies are 1 the Standard Learning Hierarchy beliefsaffectbehavior 2 the Low-Involvement Hierarchy beliefsbehavioraffect 3 and the Experiential Hierarchy. Affect behavior and cognitionaccentuates the relationship between knowing feeling and doing Solomon 2008. The ABC Model of Attitudesconsisting of the three components.
Cognition refers to the beliefs a consumer has about an attitude object. A for affective B for behavioral and C for cognitive. Behaviour involving the persons intentions to do something with regard to an attitude object.
A for affective B for behavioral and C for cognitive. Describe the ABC model of attitudes. Affect is the feeling an individual has regarding an object.
Financial Institutions Instruments and Markets 8th Edition. Structure and Function of an Attitude The first way we can examine attitudes is through a tripartite model. Refers to peoples emotions or feelings about specific attributes or overall object.
Value-expressive functionattitudes that fulfill this relate to the consumers central values or self-concept. Affect which refers to the way a consumer feels about an attitude object. In the current context affect represents the emotion or opinion about a product or service.
We employ the ABC model because it serves as a theo-retical perspective that help explain the relationship between teens and their personal. However intention does not always lead to behaviour. Beliefs about specific attributes or overall object.
Understanding Attitudes Introduction To Consumer Behaviour
The Abc Model The Decision Lab

What Is The Abc Model Of Behavior Theory Example And Tips Toolshero
0 Comments